Women
-

Seven Women in Evin Prison Speak Out Against War
•
Two separate but politically aligned statements from seven imprisoned Iranian women — all feminist and labor rights activists currently held in Tehran’s Evin Prison — have emerged, calling for an end to war, foreign aggression, and authoritarian rule. The statements sharply criticize both the Israeli government’s military assault on Iran…
-
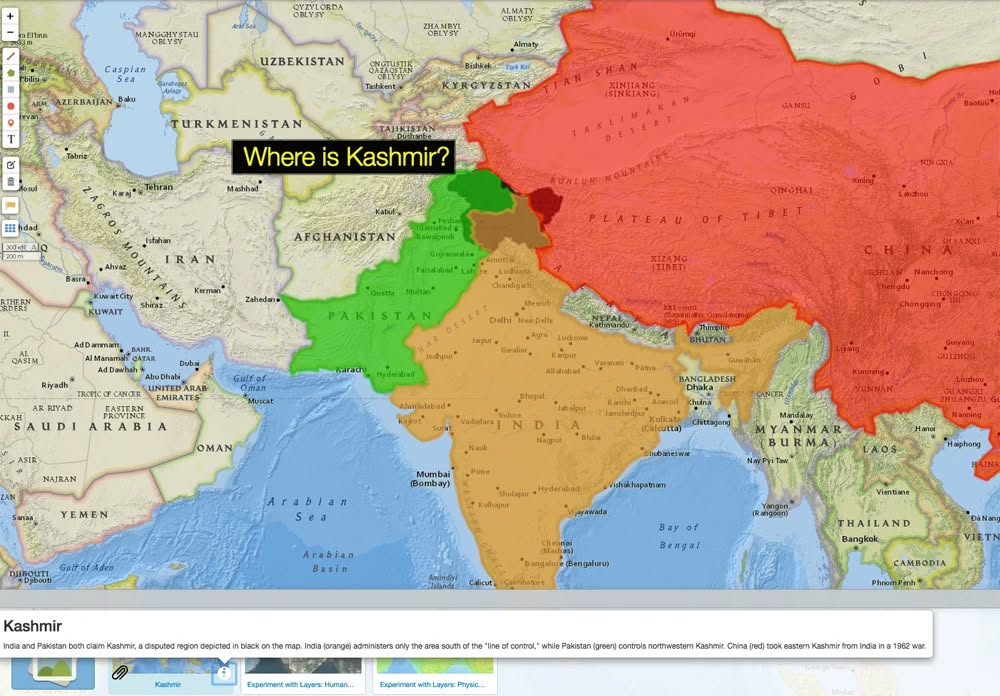
Narratives and Realities: Why Kashmir Doesn’t Fit the Script
•
I’ve followed Sahasranshu Dash for some time—initially through his public posts and online commentary. What drew me in was his clarity: sharp, unapologetic, and willing to cut through ideological noise. But it was after the April 22, 2025, suicide attack in Kashmir that his reflections began to carry a heavier…
-

A Theology of Rebellion: A Muslim Woman’s Revolt from Within
•
What happens when a Muslim woman says no to the forced hijab? What if that woman is not a secular activist or a Western journalist, but a religious scholar, a poet, and a former member of the Iranian Islamic parliament? This article introduces a Persian-language book by Sedigheh Vasmaghi, a…
-
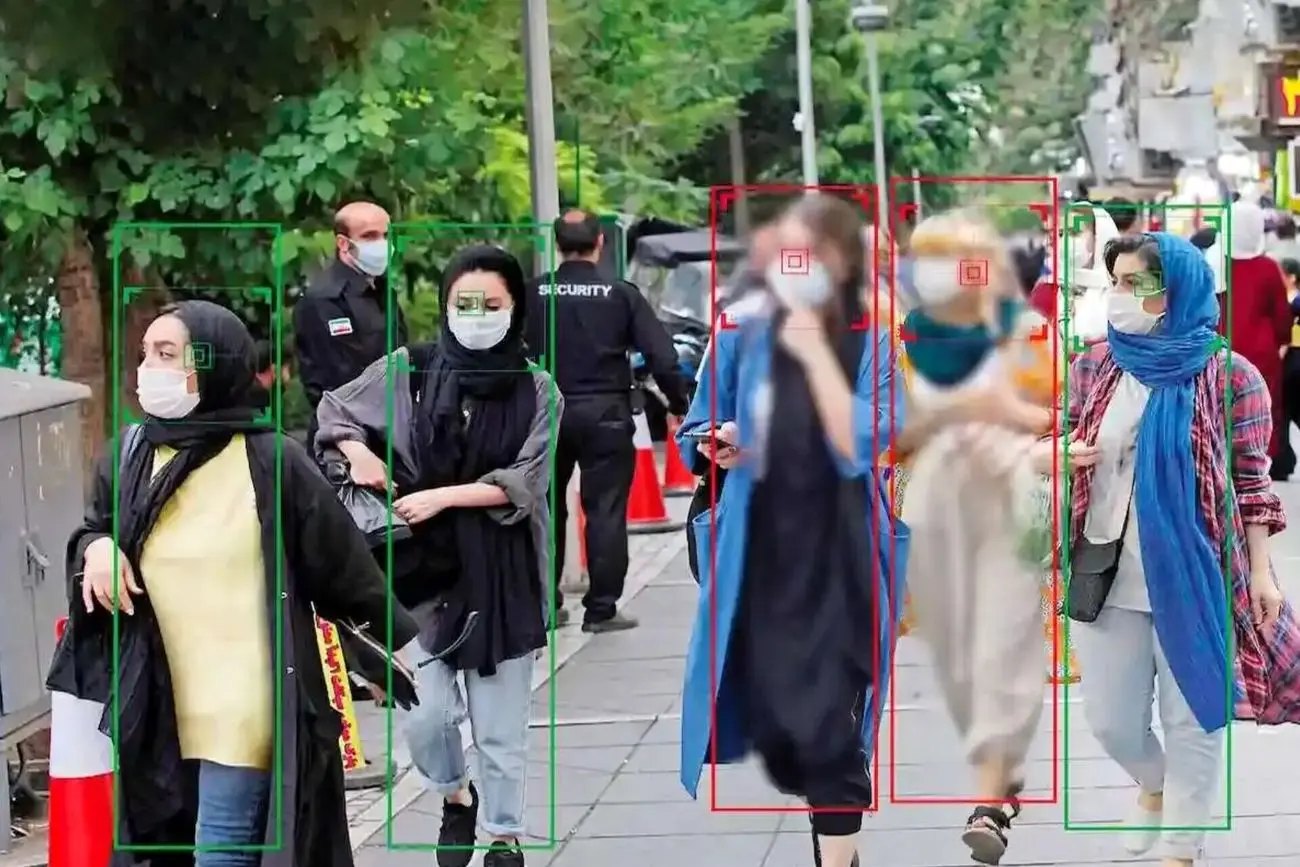

Mobile Surveillance and the War on Women’s Bodies in Iran
•
In recent years, Iran has intensified its enforcement of compulsory hijab laws through the deployment of advanced surveillance technologies. While the national implementation of these laws has faced challenges and public resistance, certain regions, notably Isfahan, have become focal points for stringent enforcement measures. Isfahan, a major city in central…
-
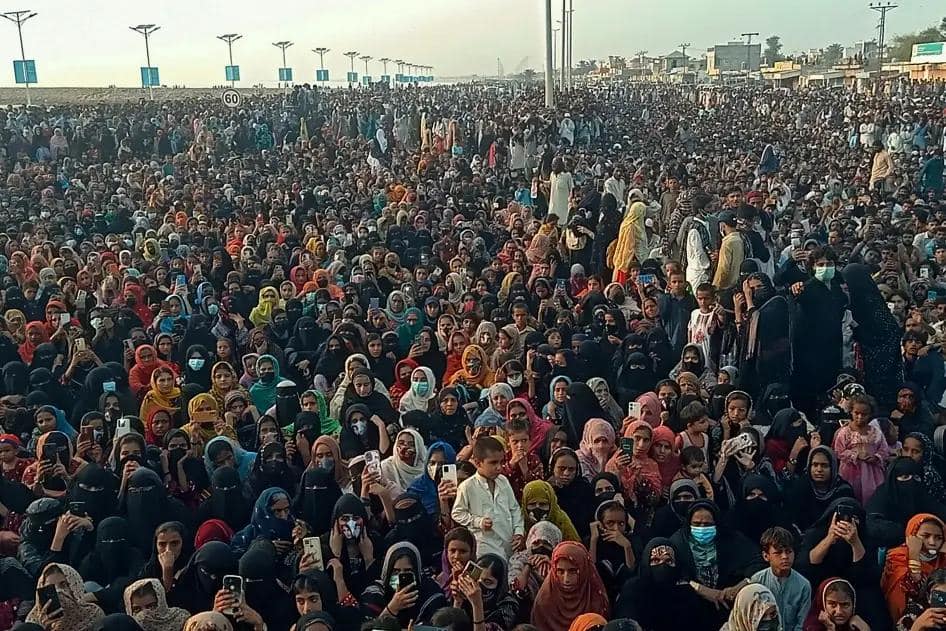

Baloch Women Face Repression for Speaking Out
•
In March 2025, two prominent Baloch human rights defenders, Mahrang Baloch and Sammi Deen Baloch, were arrested by Pakistani authorities during peaceful protests in Quetta and Karachi. Their arrests have increased concerns about the criminalization of dissent and the ongoing policy of enforced disappearances in Balochistan. Both women are internationally…
-
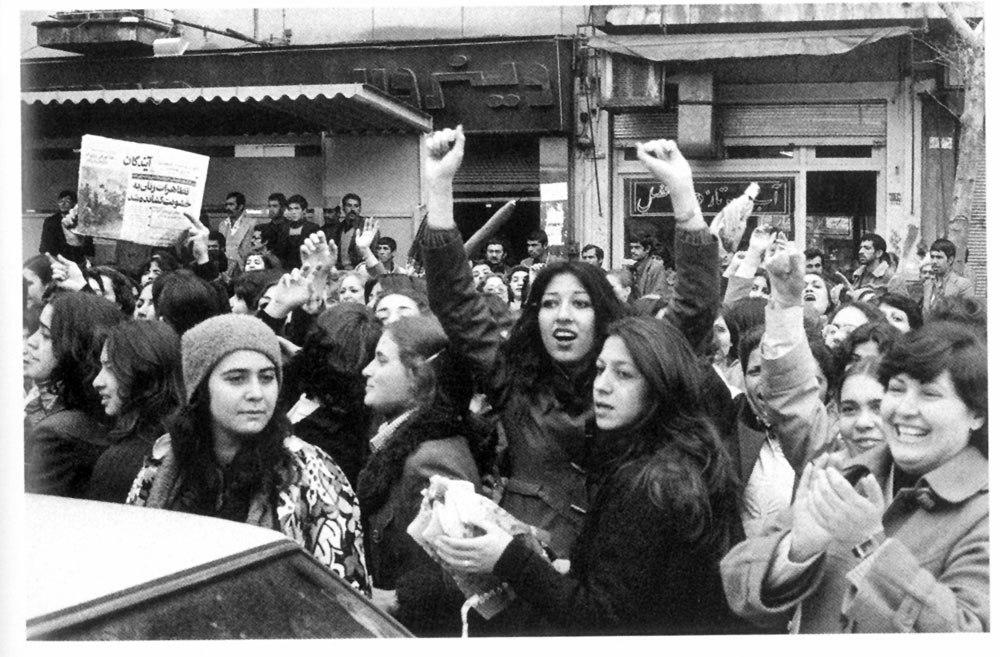

The War on Women: Beyond the Hijab of Erasure
•
In the pages of ancient manuscripts, beneath the delicate strokes of ink and gold, there is an instrument that appears again and again. Held in the hands of scholars, navigators, and mathematicians, it gleams in the soft candlelight of medieval scriptoria. The astrolabe—an intricate map of the heavens, a device…
-

The Sacred Fig and the Death of Patriarchy
•
I watched The Seed of the Sacred Fig by Mohammad Rasoulof at an alternative cinema in old town of Bern. They’re saying it’s up for the Best International Feature at the Oscars, and honestly, I see why. The story follows Iman, a man who’s spent 21 years serving the regime.…
-

Impact of the Hijab Law on Iranian Society
•
The newly approved Hijab Law in Iran, composed of 74 articles across five chapters, has ignited a storm of criticism among legal experts, citizens, journalists, and political figures. Many see it as a direct assault on individual and social freedoms, imposing restrictions that clash with the realities of daily life…
-
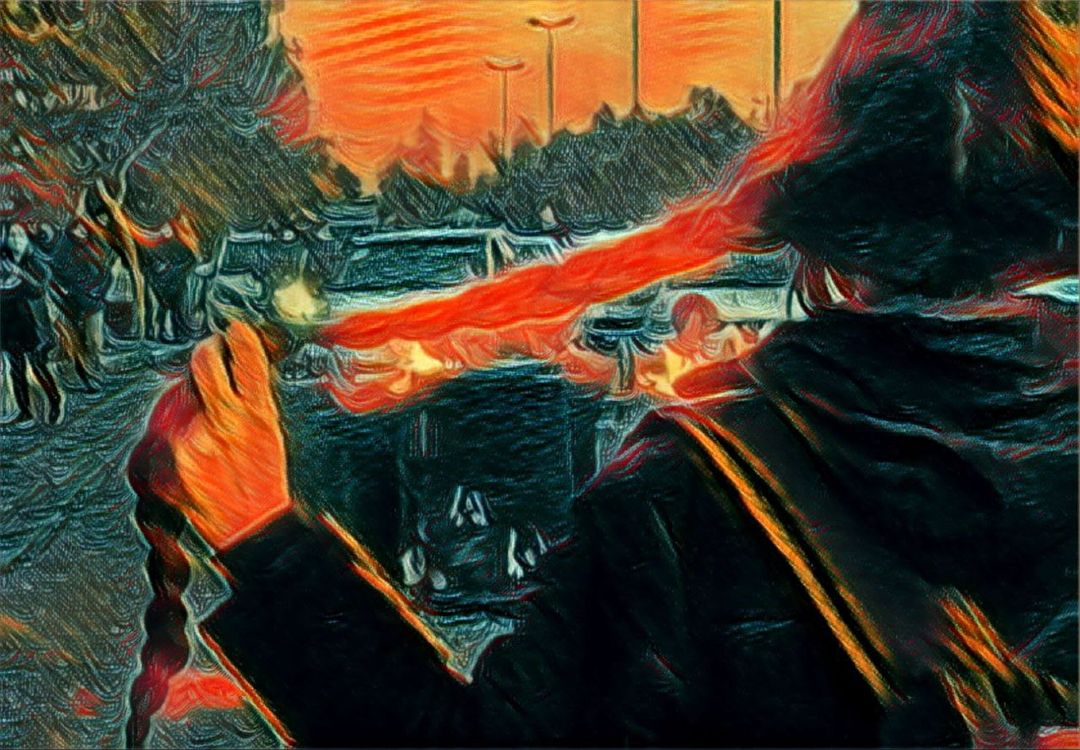

One Name, Many Lives: The Myth of the ‘Muslim Woman’
•
The story of the “Muslim woman” is not a story at all—it’s a shadow cast by politics, a construct made to fit agendas, not lives. Behind the veil of this title are millions of women with struggles as diverse as their names. But too often, these struggles are erased, replaced…
-
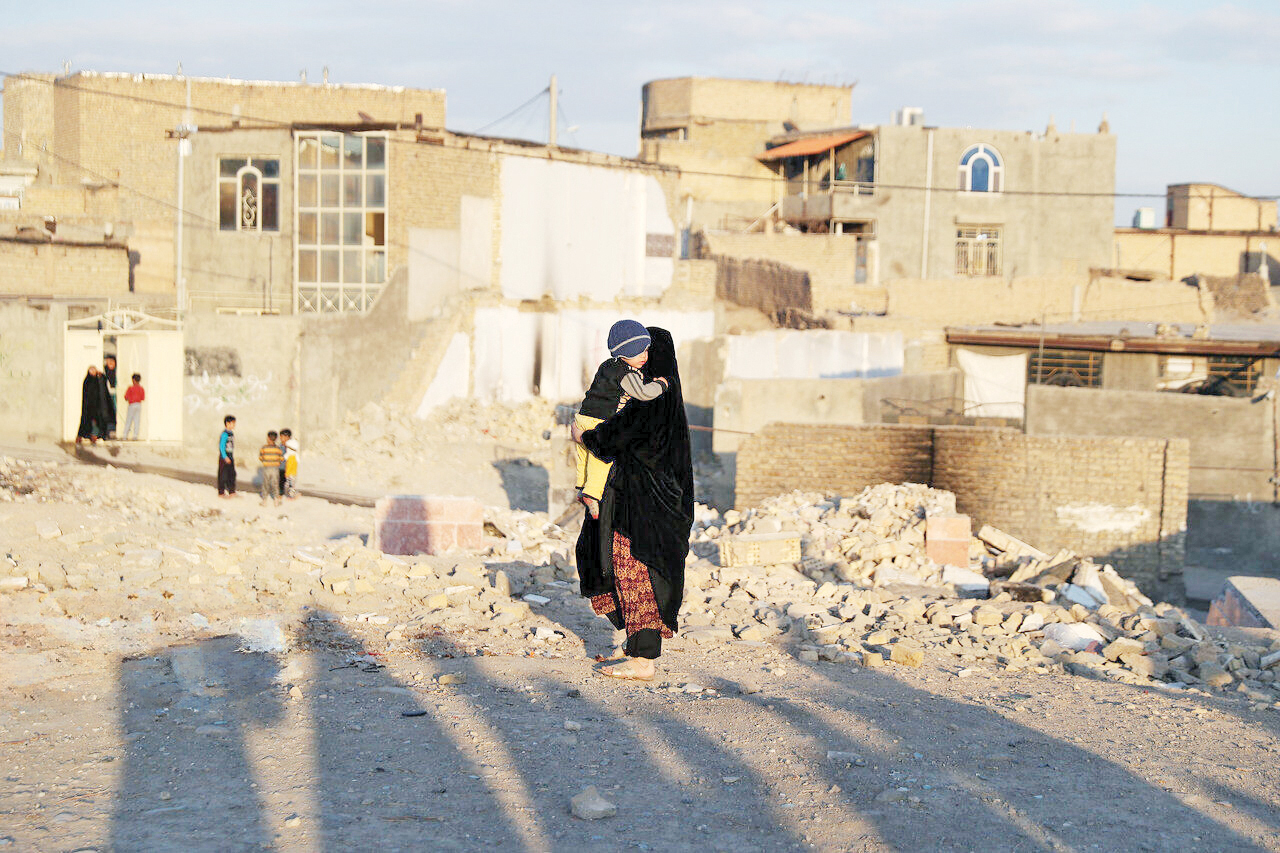

Navigating Oppression: Women’s Stories from Tehran’s Settlements
•
In the southeast shadow of Tehran, where the city’s heartbeat fades into the hum of agriculture and unpaved roads, lies Hesaramir. Its duality—a historic Upper Hesaramir and a migrant-built Turkabad—creates a kaleidoscope of lives, traditions, and struggles. Yet, the soul of this settlement is found in its women, whose voices,…
-

Femicide Crisis in Iran: Understanding the Urgent Need for Change
•
In just two days, two cases of femicide have shaken Iran. First, a lawyer murdered his journalist wife, Mansoureh Ghadiri Javi with brutal blows from a knife and dumbbell. In another case, another male lawyer killed his wife and son before ending his own life. According to the Iranian newspaper…
-
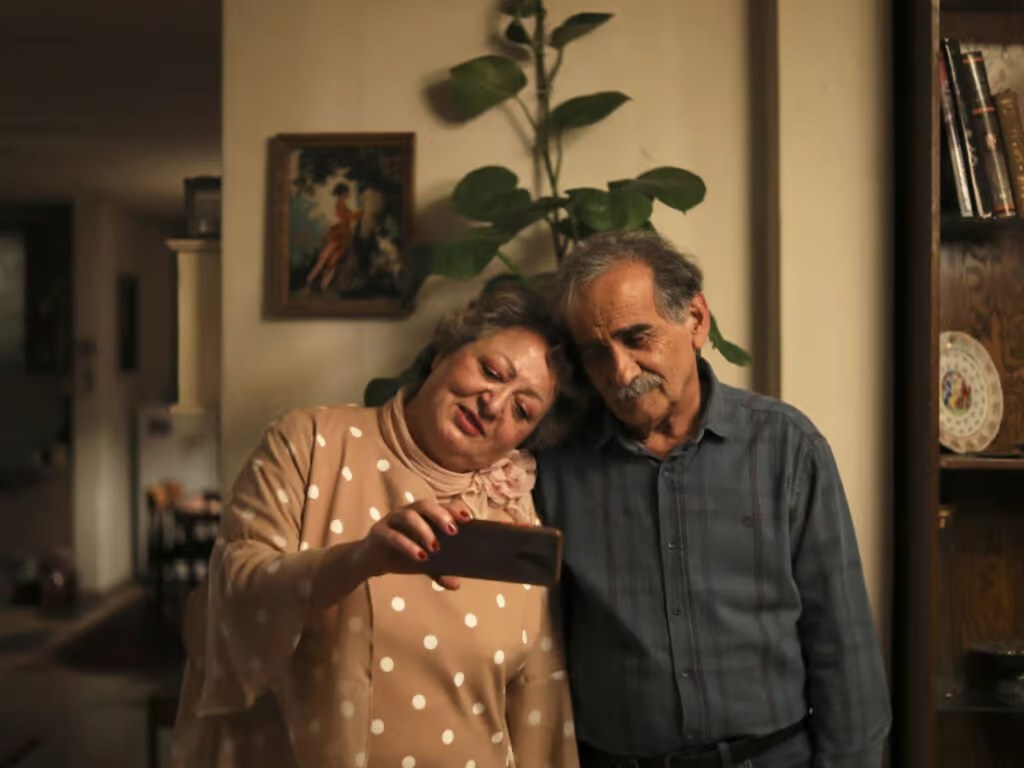

My Favorite Cake: Cinema, Memory, and Resistance in Iran
•
For some time now, My Favorite Cake, directed by Maryam Moghadam and Behtash Sanaeeha, has been available to the public through some Telegram channels. After receiving attention in the 74th Berlin Film Festival’s cinema circles, audiences now have easy access to this film. My Favorite Cake draws power from its…